The 2020 census figures are in, and Indiana’s population grew by nearly a third of a million Hoosiers over the last 10 years. While many were hopeful this might be the decade Indiana would reach the 7 million mark, we fell short of that at 6,785,528 residents. Some of the largest areas of growth were in the donut counties surrounding Indianapolis – specifically Hamilton, Hancock, Johnson, Hendricks and Boone – as well as Tippecanoe, Allen and Lake counties.
What do the decennial changes in population mean for your local public library? Over the next year or two, some patrons and staff might see changes in hours or requirements for future hires. Public libraries in Indiana are required to meet a set of standards required by statute, based on the size of their population service area. These standards dictate levels of service, including the number of hours a library must be open, as well as minimum staff qualifications related to education and experience for professional positions.
 In Indiana, public libraries serving over 40,000 residents are considered Class A libraries, while mid-sized libraries serving 10,000-39,999 residents are Class B, and those serving fewer than 10,000 are Class C libraries. Just for perspective, over half, or 128 out of the 236 public libraries statewide, are Class C libraries with the lesser requirements.
In Indiana, public libraries serving over 40,000 residents are considered Class A libraries, while mid-sized libraries serving 10,000-39,999 residents are Class B, and those serving fewer than 10,000 are Class C libraries. Just for perspective, over half, or 128 out of the 236 public libraries statewide, are Class C libraries with the lesser requirements.
Indiana public library classes are reevaluated every 10 years following the decennial census. A change in service population can affect a library’s class size, causing the library to need to reexamine their service models to accommodate the new or lost residents. In 2020, five public library systems – Goshen, LaGrange, Newburgh Chandler, West Lafayette and Westfield-Washington – increased their class size, while four systems moved down a class. For those who moved up a class, some will find they need to increase their hours, and staff accepting new positions may need to meet minimum educational requirements set in Indiana’s certification rules. This information was communicated to the affected directors in a letter from the Indiana State Library.
Indiana public libraries receive a majority of their funding through property tax dollars, so changes in population may also gradually affect a library’s tax base. Areas that have lost population may subsequently have lost funding, which disproportionately affects the smallest libraries in the state, many of whom serve fewer than 3,000 residents.
Finally, individuals who do not live in a public library service area who purchase non-resident cards may find that their fee has changed. That is because each library’s non-resident fee is based on the library’s cost per capita in the previous year, which will now be based on the 2020 population.
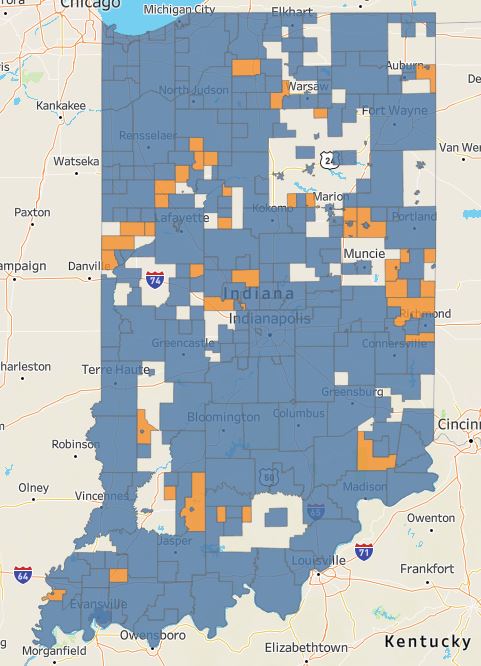 A table showing service area population changes for each library district from 2010 to 2020 can be viewed here.
A table showing service area population changes for each library district from 2010 to 2020 can be viewed here.
Evaluating the census data also gave STATS Indiana a chance to update the interactive map of public library districts and contract areas in the state, which can be viewed here.
A special thanks to Katherine Springer, state data coordinator, for her assistance collaborating with the Indiana Business Research Center to examine and compile the 2020 census data for libraries. Thanks also to Angela Fox for providing public library survey data that served as the basis for determining library districts.
Libraries with questions about their service areas can contact Jen Clifton in the Indiana State Library’s Library Development Office.
This blog post was written by Jen Clifton, Library Development Office director.
