Not everyone lives close enough to come to the one state fair in their state, which is why county fairs are so important. They’re a feasible way to bring local people together for an exchange of ideas, foods, farming and fun. Though the first Indiana State Fair occurred in 1852, the idea of the county fair was one that had been tried by local agricultural associations in Indiana since the 1830s.1 2 Sensing a need for a way for farming families to come together, the agricultural associations came up with the idea of a county fair so that these farming communities could exchange agricultural methods, personally developed farming implements, homemade culinary ideas and more. Though the idea was widespread, the passion for these events from the locals themselves just wasn’t there and most of these early fairs folded before the 1850s. However, with the emergence of the Indiana State Fair, and the continued success that it maintained, many smaller agricultural associations decided it would be worth the risk to try again and bring back their smaller county fairs. Only this time, the concept stuck, and enjoyment of the county fair would be something that the people from the 1850s and the Hoosiers of today still have in common.
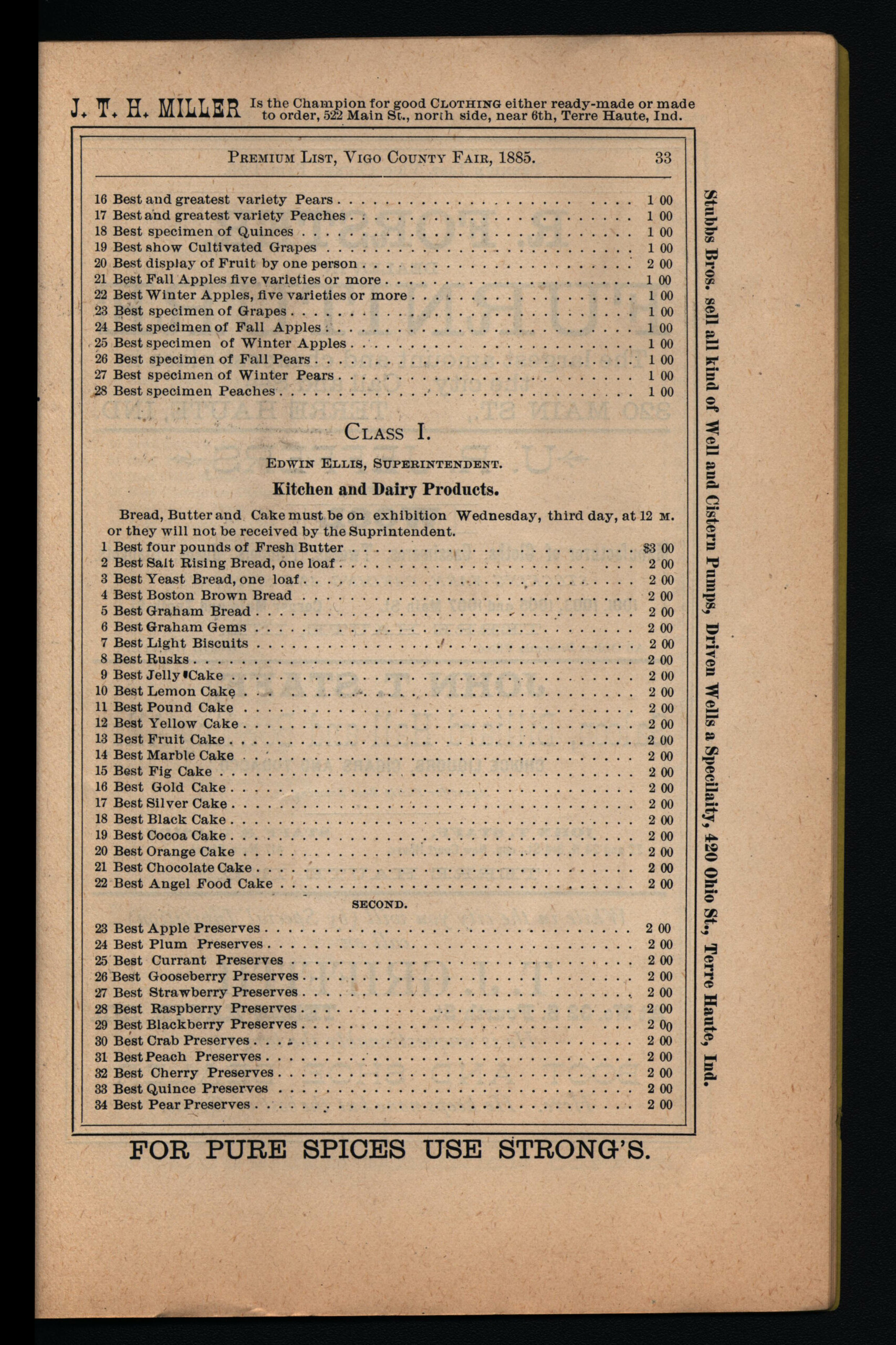
The draws for many to come to these county fairs wasn’t to relax, but to compete. When many of the county fairs came back, they came back with a draw for the farming families in the area. Premiums, or monetary rewards for winning different types of competitions, were offered for all sorts of different types of contests. The earliest Premium List that we have at the Indiana State Library comes from the Tippecanoe County Fair in 1871 and has a listed $3,500 in premiums being given out, slightly more than $87,000 today.3 Showing how much some of these fairs were growing, just a decade later the Tippecanoe County Fair would be giving out over $7,000 in prizes, more than $223,000 today. Entry tickets back then were actual paper tags that were tied in a visible spot on the fair patron’s clothing or wrist. Prices were usually 25 cents throughout the 1800s and it was typically another 10 cents to stable or tie up your horse and carriage. Animal showing competitions, which are still a staple in many county fairs today, were by far the biggest draw in terms of different types of animals to show and prizes received.
Horse racing competitions were an early staple of the fair throughout the state and premiums were extremely high for these no matter the county. There were also early competitions in fabric making, artistry, farm implement craftmanship, artisanship, cooking, clothes crafting and more. The competitions would change depending on the materials of the local communities.
The list of the premiums would be sent out as a flyer before the fair containing the competitions available, rules and regulations of the fair and competitions, the prizes for each, and of course, tons of advertising. These advertisements in the Premium Lists are incredibly diverse. Ranging from boots, embalming services and animal feed to clocks, jewelry and fine glassware; the advertisements can tell us a lot about what the people of the times, needed or were interested in. And when it came to trying to make sure interest was always high, more and varying types of competitions and sideshow attractions were brought to the county fairs. Ladies’ Work, the categories of competition being stereotypically limited by their times, became popularized throughout the 1870s. The Ladies’ Work events were mostly linked to competing in arenas such as embroidery and needlework, flower arrangement, wig and hair work, women’s clothing and small furniture making. Though most of these competitions would only be giving out diplomas of victory to the women, not actual premiums until the 1880s. Competitions were specifically put in place so that children could have an arena of their own to show off their young skills. During the 1890s, musical acts or performers became a common event during the fair days.
County fairs in Indiana would continue to adapt and connect their local communities throughout the 1900s following their reemergence in the 1850s. They would adapt technology to bring tractor pulls, stock car races and carnival rides to the scene, a far cry from the early trading of farming implements.4 Performers from across the country would soon be paid to come and play at these local venues, giving Hoosiers a taste of the wider entertainment scene. Almost 170 years later, the tradition of the county fair is something that every single one of the 92 counties in Indiana offer to everyone.5 They occur mostly in June or July, though Lake and Dekalb counties have theirs in August and September respectively. Click here to see the 2023 Indiana county fair dates.
So, with a bit of history narrated, it’s now time to go out this summer and experience a slice of a local Indiana community by visiting one of our many wonderful county fairs in Indiana!
This blog post was written by Rare Books and Manuscripts program coordinator A.J. Chrapliwy.
1.Jackson, Steven. (2010, July 03). “In History: Madison County’s legacy of fairs.” The Herald Bulletin. Retrieved on May 15, 2023, from In History: Madison County’s legacy of fairs | MAD Life | heraldbulletin.com.
2.Hale, Michelle. (1994) “Marion County Fair.” Indyencyclopedia. Retrieved on May 15, 2023, from Marion County Fair – indyencyclopedia.org.
3.Webster, Ian. (2023, May 17) “Inflation Calculator.” Official Inflation Data, Alioth Finance. Retrieved on May 15, 2023, from U.S. Inflation Calculator: 1635→2023, Department of Labor data (officialdata.org).
4.Conybeare, Brian. (2018, July 20) “History of the Elkhart County 4-H Fair.” ABC57. Retrieved on May 15 2023, from History of the Elkhart County 4-H Fair (abc57.com).
5.“Indiana Association of Fairs and Festivals.” (2023) 2023 4-H County Fair Dates. Indiana Fairs and Festivals. Retrieved on May 15, 2023, from 2023 4-H County Fair Dates (indianafairsandfestivals.org).